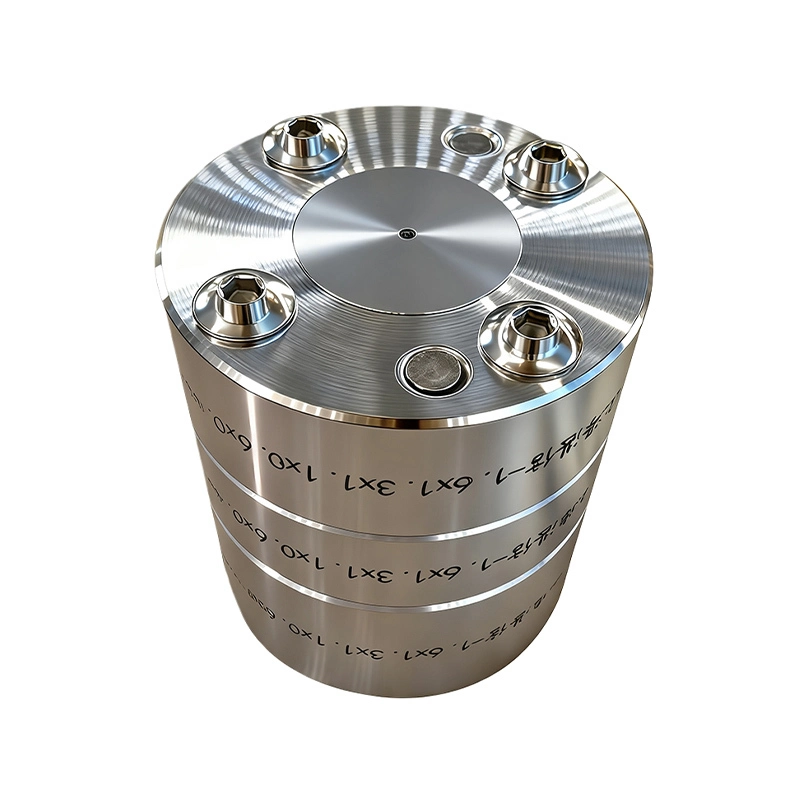
Polymer Fiber Spinning, Sol-Gel Sintering Spinning Spinneret
Typical architecture and flow paths
Coaxial or multi-coaxial structure: spinning spinneret annulus for the sol/slurry, center for the bore fluid; optional additional coaxial ring for external coagulant or a sheath flow.
High solids/thixotropic feed compatibility: spinneret enlarged, rigid, and wear resistant annulus and orifice; wear-resistant liners (zirconia/tungsten carbide/sapphire); polished wetted surfaces plus anti-wear coatings to mitigate particle abrasion and clogging.
low shear, low holdup design: Trustech spinneret gently curved distribution channels and a diffusion/ flow straightening chamber to reduce shear induced gelation, flocculation, or bridging.
Gelation trigger interface: a coaxial sleeve flow of external coagulant near the orifice or a short free gap to coagulation bath to achieve rapid gelation and shape fixing; optional outer shielding liquid to stabilize the free surface of Trstech spinning spinneret.
Thermal management and degassing: spinneret need upstream temperature control jacket and vacuum degassing port to suppress bubbles and thermally induced viscosity jumps.
Structural Features Structural features and process essentials
Trustech Spinneret Key Design Elements Trustech
These parameters are fundamental to spinneret design and directly determine the membrane's final performance
|
Parameter |
Description |
Influence on membrane performance |
| Flow channel (R) | The runner for transporting, buffering, and distributing the dope and bore fluids. | Different structures should be optimized according to material properties, viscosity, spinneret orifice size, and hole quantities to achieve optimal spinning performance. |
| Annular gap width (d) | The gap (thickness) of the dope flow channel. | It primarily determines the hollow fiber wall thickness. Narrower gaps yield thinner walls and lower mass-transfer resistance, but may reduce mechanical strength. |
| Bore tube outer diameter (d₁) | The outer diameter of the central tube forming the inner wall of the annular gap. | Together with the outer sleeve inner diameter, it defines the annular gap width. |
| Outer sleeve inner diameter (d₂) | The inner diameter of the spinneret outer sleeve forming the outer wall of the annular gap. | Together with the bore tube outer diameter, it defines the annular gap width and the fiber outer diameter. |
| Central tube inner diameter (d₃) | The diameter of the bore fluid channel. | It primarily determines the fiber inner diameter. The inner diameter affects membrane module packing density and the pressure drop of fluid inside the fiber. |
| Length-to-gap ratio (L/d) | The ratio of the flow channel length (L) to the annular gap width (d). | It affects spinning stability. Designing an appropriate L/d according to material properties and process conditions helps stabilize flow and eliminate entry effects, resulting in more uniform extruded fibers membrane. |
| Concentricity | The coaxial alignment among the dope layer inner diameter at the spinneret outlet and the bore tube inner and outer diameters. | It affects wall-thickness uniformity and bubble point pressure. |
| Extrusion face geometry | The foremost geometry of the spinneret, such as flat or micro-tapered. | It influences draw-down and deformation after extrusion, especially important for the air-gap segment in dry-wet spinning. |
The Advantages of Trustech FCT Generation 5th Spinneret Trustech
Wear resistant and anti-clogging, compatible with high solids slurries: Nozzles and liners made from ultra-hard materials (zirconia, tungsten carbide, sapphire), with polished surfaces and anti-wear coatings, resist particle abrasion and clogging, ensuring stable delivery of high solids, viscous sols/slurries.
Low shear and rapid gel-forming: Gently curved distribution channels and a coaxial external gelling agent flow or short air-gap design significantly reduce shear stress to prevent premature gel aggregation; rapid gelation at the nozzle exit forms a robust green fiber wall, avoiding collapse and ovalization.
Multilayer co-extrusion with controlled shrinkage compensation: Supports multilayer co-extrusion (dense skin + porous support), producing composite ceramic/metal/glass hollow fibers in a single pass; spinneret dimensions and wall-thickness are pre-compensated for 10–40% drying/sintering shrinkage, maintaining dimensional accuracy and structural integrity after high-temperature sintering (400–1200°C).
Product Parameters
|
Brand |
Trustech |
Application |
Sol-Gel Sintering |
| Material | SUS304, SUS630, SUS316L | Holes/Pack | Single |
| Dope inlet Thread | G1/8, BSP1/8, NPT1/8 | Minimum membrane OD | 1.0mm |
| Bore liquid inlet thread | G1/8, BSP1/8, NPT1/8 | Customize thread | Yes |
| Precision | ±0.002mm | Concentricity | 0.003mm |
| Design | Conventional design | Connections | Standard |
| Viscosity application | 1000-300000cp | Roughness | Ra0.2-0.8 |
| Solvent | DMAC, DMF, NMP | Temperature | 150℃ |
Suitable Materials
PVDF (Polyvinylidene Fluoride), CA (cellulose acetate), PVC (Polyvinyl chloride), PES (Polyethersulfone), PSF/PSU (Polysulfone), PA (Nylon, Polyamide), PAN (polyacrylonitrile)
Key design parameter references (one of customer process as example)
Annular gap height: typically 150–300 μm for polymer systems; for sol–gel, relax to about 200–800 μm to resist clogging and maintain flow.
Coaxiality: ≤5-10μm ,the smaller, the better; for multi-hole arrays, inter hole flow variation ≤±3%.
Material selection: 316L/17-4PH stainless steel body;
Cleaning and maintenance: solvent flushing and ultrasonics for polymer systems; for sol–gel, solvent/dispersant recirculation plus mechanical passage clearing.
Common Specifications
| No. | General Specification | Application | Design Type | Type |
| 1 | 1.3/0.7/0.4 | Sol-Gel Sintering | Conventional design | Single-aperture/ Multi-aperture |
| 2 | 1.3/0.8/0.5 | Sol-Gel Sintering | Conventional design | Single-aperture/ Multi-aperture |
| 3 | 1.3/1.0/0.7 | Sol-Gel Sintering | Conventional design | Single-aperture/ Multi-aperture |
| 4 | 1.4/0.7/0.4 | Sol-Gel Sintering | Conventional design | Single-aperture/ Multi-aperture |
| 5 | 1.4/0.9/0.6 | Sol-Gel Sintering | Conventional design | Single-aperture/ Multi-aperture |
| 6 | 1.4/1.0/0.8 | Sol-Gel Sintering | Conventional design | Single-aperture/ Multi-aperture |
| 7 | 1.6/0.8/0.5 | Sol-Gel Sintering | Conventional design | Single-aperture/ Multi-aperture |
| 8 | 1.6/0.9/0.6 | Sol-Gel Sintering | Conventional design | Single-aperture/ Multi-aperture |
| 9 | 1.8/0.9/0.5 | Sol-Gel Sintering | Conventional design | Single-aperture/ Multi-aperture |
| 10 | 1.8/1.2/0.6 | Sol-Gel Sintering | Conventional design | Single-aperture/ Multi-aperture |
| 11 | 1.8/1.2/0.8 | Sol-Gel Sintering | Conventional design | Single-aperture/ Multi-aperture |
| 12 | 2.3/1.5/1.0 | Sol-Gel Sintering | Conventional design | Single-aperture/ Multi-aperture |
| 13 | 2.3/1.5/1.2 | Sol-Gel Sintering | Conventional design | Single-aperture/ Multi-aperture |
| 14 | 2.7/1.5/1.2 | Sol-Gel Sintering | Conventional design | Single-aperture/ Multi-aperture |
| 15 | 2.2/1.7/1.4 | Sol-Gel Sintering | Conventional design | Single-aperture/ Multi-aperture |
| 16 | 2.7/2.2/1.9 | Sol-Gel Sintering | Conventional design | Single-aperture/ Multi-aperture |
| 17 | 2.8/2.0/1.5 | Sol-Gel Sintering | Conventional design | Single-aperture/ Multi-aperture |
| 18 | 2.8/2.2/1.9 | Sol-Gel Sintering | Conventional design | Single-aperture/ Multi-aperture |
| 19 | 2.8/2.3/2.0 | Sol-Gel Sintering | Conventional design | Single-aperture/ Multi-aperture |
| 20 | 2.9/1.4/1.1 | Sol-Gel Sintering | Conventional design | Single-aperture/ Multi-aperture |
| 21 | 2.9/1.8/1.5 | Sol-Gel Sintering | Conventional design | Single-aperture/ Multi-aperture |
| 22 | 2.9/1.9/1.6 | Sol-Gel Sintering | Conventional design | Single-aperture/ Multi-aperture |
| 23 | 3.0/2.3/1.9 | Sol-Gel Sintering | Conventional design | Single-aperture/ Multi-aperture |
| 24 | 3.0/2.3/2.0 | Sol-Gel Sintering | Conventional design | Single-aperture/ Multi-aperture |
| 25 | 3.1/2.8/2.5 | Sol-Gel Sintering | Conventional design | Single-aperture/ Multi-aperture |
| 26 | 3.2/2.2/1.8 | Sol-Gel Sintering | Conventional design | Single-aperture/ Multi-aperture |
| 27 | 3.4/1.7/1.4 | Sol-Gel Sintering | Conventional design | Single-aperture/ Multi-aperture |
| 28 | 3.4/2.2/1.8 | Sol-Gel Sintering | Conventional design | Single-aperture/ Multi-aperture |
| 29 | 3.7/1.9/1.6 | Sol-Gel Sintering | Conventional design | Single-aperture/ Multi-aperture |
| 30 | 3.8/2.2/1.9 | Sol-Gel Sintering | Conventional design | Single-aperture/ Multi-aperture |
| 31 | 3.8/2.3/2.0 | Sol-Gel Sintering | Conventional design | Single-aperture/ Multi-aperture |
Customer Membrane Examples
ACHIEVEMENTS
FAQ
About Trustech