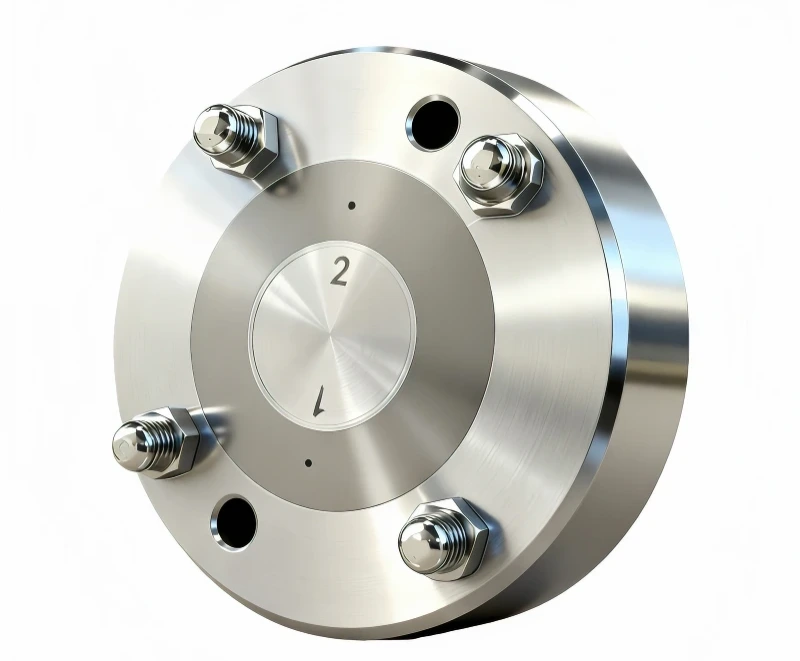
Polymer Fiber Spinning, Melt Spinning Spinneret
Melt Extrusion Spinneret, also called melt Spinning Spinnerette is a core precision component in melt-spinning processes. It forces high temperature polymer melts (e.g., PET polyester, PP polypropylene, PA nylon, PI polyimide) through micro-fabricated orifices under high pressure,typically with diameters from tens of micrometers up to a few millimeters,to uniformly extrude continuous filaments, fibers, or films. Its design must address three key challenges: uniform distribution of the high temperature melt, precise shaping and control, and resistance to corrosion and wear.
Working Principle
Melt delivery
Polymers (e.g., PET, PA, PP) are heated in an extruder to a molten, viscous state.
Metering and pressurization
The melt is precisely metered and fed into the spinneret assembly. Internal distribution channels are designed to deliver the melt uniformly and steadily to each capillary.
Shear and extrusion
Under high pressure, the melt is forced through extremely small capillaries typically 0.28–1.5 mm in diameter. This imposes strong shear, orienting polymer chains to some extent along the flow direction.
Die swell (Barus effect)
Upon exiting the capillary, elastic recovery causes the filament diameter to expand slightly.
Trustech Spinneret Key Design Elements Trustech
These parameters are fundamental to spinneret design and directly determine the membrane's final performance
|
Parameter |
Description |
Influence on membrane performance |
| Flow channel (R) | The runner for transporting, buffering, and distributing the dope and bore fluids. | Different structures should be optimized according to material properties, viscosity, spinneret orifice size, and hole quantities to achieve optimal spinning performance. |
| Annular gap width (d) | The gap (thickness) of the dope flow channel. | It primarily determines the hollow fiber wall thickness. Narrower gaps yield thinner walls and lower mass-transfer resistance, but may reduce mechanical strength. |
| Bore tube outer diameter (d₁) | The outer diameter of the central tube forming the inner wall of the annular gap. | Together with the outer sleeve inner diameter, it defines the annular gap width. |
| Outer sleeve inner diameter (d₂) | The inner diameter of the spinneret outer sleeve forming the outer wall of the annular gap. | Together with the bore tube outer diameter, it defines the annular gap width and the fiber outer diameter. |
| Central tube inner diameter (d₃) | The diameter of the bore fluid channel. | It primarily determines the fiber inner diameter. The inner diameter affects membrane module packing density and the pressure drop of fluid inside the fiber. |
| Length-to-gap ratio (L/d) | The ratio of the flow channel length (L) to the annular gap width (d). | It affects spinning stability. Designing an appropriate L/d according to material properties and process conditions helps stabilize flow and eliminate entry effects, resulting in more uniform extruded fibers membrane. |
| Concentricity | The coaxial alignment among the dope layer inner diameter at the spinneret outlet and the bore tube inner and outer diameters. | It affects wall-thickness uniformity and bubble point pressure. |
| Extrusion face geometry | The foremost geometry of the spinneret, such as flat or micro-tapered. | It influences draw-down and deformation after extrusion, especially important for the air-gap segment in dry-wet spinning. |
The Advantages of Trustech FCT Spinneret Trustech
Uniform melt distribution and forming for high fiber consistency: Precision flow distribution and micro-capillary design ensure the high temperature melt is evenly delivered and steadily extruded across all orifices, reducing denier variation and off size defects, and improving product uniformity and yield.
Precise control of dimensions and cross sections, supporting multiple sizes and shapes: Micron-scale capillaries and optimized flow channels control shear and residence time, balancing extrusion stability with compensation for die swell (Barus effect), enabling accurate forming from tens of micrometers to millimeter-scale diameters in round or profiled cross-sections.
High temperature, corrosion, and wear resistance for long life and low maintenance: Uses high temperature alloys/coatings and wear and corrosion resistant materials. The structure resists thermal shock and chemical attack, suitable for continuous high pressure operation with polymers such as PET, PP, PA, and PI, reducing downtime and total lifecycle cost.
Product Parameters
|
Brand |
Trustech |
Application |
TIPS/Melting |
| Material | SUS304, SUS630, SUS316L | Holes/Pack | Single |
| Dope inlet Thread | G1/8, BSP1/8, NPT1/8 | Minimum membrane OD | 0.20mm |
| Bore liquid inlet thread | G1/8, BSP1/8, NPT1/8 | Customize thread | Yes |
| Precision | ±0.002mm | Concentricity | 0.003mm |
| Design | Conventional design/ FCT design | Connections | Standard |
| Viscosity application | 1000-300000cp | Roughness | Ra0.2-0.8 |
| Solvent | No | Temperature | 260℃ |
Suitable Materials
PET(Polyethylene Terephthalate), PP (Polypropylene), PA6( Polyamide 6 ), PE (Polyethylene), PLA (Polylactide),TPU (Thermoplastic Polyurethane), PPS (Polyphenylene Sulfide), PTT (Polytrimethylene Terephthalate), PBT (Polybutylene Terephthalate), PVA (Polyvinyl Alcohol ), PAN (Polyacrylonitrile ), PEEK (Polyether Ether Ketone), PVDF-HFP( Poly vinylidene fluoride-co-hexafluoropropylene)
Common Specifications
| No. | General Specification | Application | Design Type | Type |
| 1 | 1.4/0.8/0.6 | TIPS/Melting | Conventional design/ FCT design | Single-aperture/ Multi-aperture |
| 2 | 1.5/0.9/0.6 | TIPS/Melting | Conventional design/ FCT design | Single-aperture/ Multi-aperture |
| 3 | 1.6/1.0/0.6 | TIPS/Melting | Conventional design/ FCT design | Single-aperture/ Multi-aperture |
| 4 | 1.8/1.1/0.5 | TIPS/Melting | Conventional design/ FCT design | Single-aperture/ Multi-aperture |
| 5 | 1.9/1.2/0.6 | TIPS/Melting | Conventional design/ FCT design | Single-aperture/ Multi-aperture |
| 6 | 2.0/1.0/0.7 | TIPS/Melting | Conventional design/ FCT design | Single-aperture/ Multi-aperture |
| 7 | 3.1/1.8/1.5 | TIPS/Melting | Conventional design/ FCT design | Single-aperture/ Multi-aperture |
| 8 | 3.1/1.8/1.5 | TIPS/Melting | Conventional design/ FCT design | Single-aperture/ Multi-aperture |
| 9 | 3.2/2.2/1.8 | TIPS/Melting | Conventional design/ FCT design | Single-aperture/ Multi-aperture |
| 10 | 3.3/1.1/0.9 | TIPS/Melting | Conventional design/ FCT design | Single-aperture/ Multi-aperture |
| 11 | 3.4/2.4/2.0 | TIPS/Melting | Conventional design/ FCT design | Single-aperture/ Multi-aperture |
Customer Membrane Examples
ACHIEVEMENTS
FAQ
About Trustech