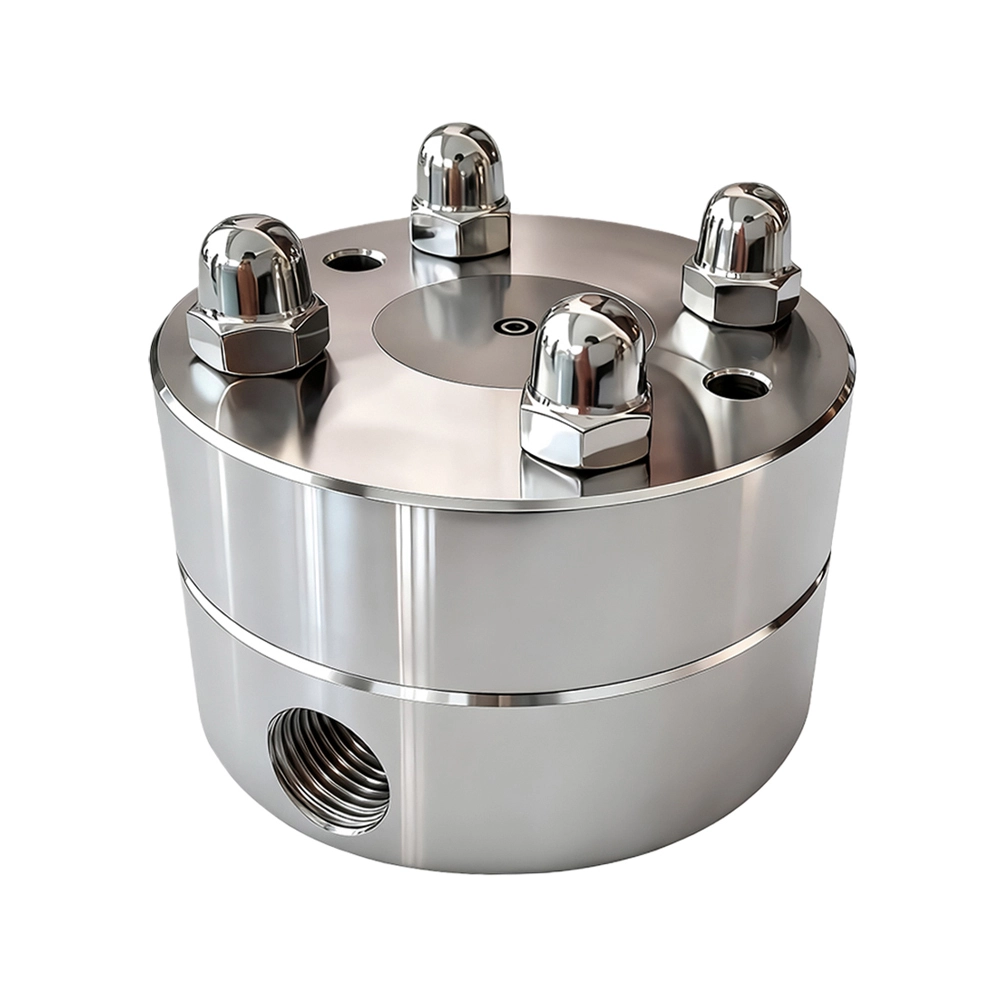
Hollow Fiber spinning Spinneret,TIPS spinning Spinneret
Structural Features
Solution preparation: Above the polymer's melting point, dissolve the polymer in a high boiling, low volatility solvent as a diluent state to form a homogeneous solution. For example, polypropylene (PP) must be dissolved at temperatures above its melting point (about 165°C).
Phase separation process: After extrusion through the spinning spinneret, cooling triggers phase separation:
Solid–liquid phase separation (S–L): the polymer crystallizes out to form the continuous phase, with the solvent as the dispersed phase.
Liquid–liquid phase separation (L–L): the polymer and solvent form a biphasic structure; the polymer rich phase constitutes the membrane matrix, while the polymer lean phase forms the pores.
Solvent extraction: Use a volatile agent (e.g., ethanol) to extract the diluent, yielding a polymer membrane with a microporous structure.
Functional features
The module design of flow rate control of FCT generation 6th hollow fiber spinneret is simple in structure and easy to operate, each spinneret hole can be individually controlled.
Trustech Spinneret Key Design Elements Trustech
These parameters are fundamental to spinneret design and directly determine the membrane's final performance:
|
Parameter |
Description |
Influence on membrane performance |
| Flow channel (R) | The runner for transporting, buffering, and distributing the dope and bore fluids. | Different structures should be optimized according to material properties, viscosity, spinneret orifice size, and hole quantities to achieve optimal spinning performance. |
| Annular gap width (d) | The gap (thickness) of the dope flow channel. | It primarily determines the hollow fiber wall thickness. Narrower gaps yield thinner walls and lower mass-transfer resistance, but may reduce mechanical strength. |
| Bore tube outer diameter (d₁) | The outer diameter of the central tube forming the inner wall of the annular gap. | Together with the outer sleeve inner diameter, it defines the annular gap width. |
| Outer sleeve inner diameter (d₂) | The inner diameter of the spinneret outer sleeve forming the outer wall of the annular gap. | Together with the bore tube outer diameter, it defines the annular gap width and the fiber outer diameter. |
| Central tube inner diameter (d₃) | The diameter of the bore fluid channel. | It primarily determines the fiber inner diameter. The inner diameter affects membrane module packing density and the pressure drop of fluid inside the fiber. |
| Length-to-gap ratio (L/d) | The ratio of the flow channel length (L) to the annular gap width (d). | It affects spinning stability. Designing an appropriate L/d according to material properties and process conditions helps stabilize flow and eliminate entry effects, resulting in more uniform extruded fibers membrane. |
| Concentricity: | The coaxial alignment among the dope layer inner diameter at the spinneret outlet and the bore tube inner and outer diameters. | It affects wall-thickness uniformity and bubble point pressure. |
| Extrusion face geometry | :The foremost geometry of the spinneret, such as flat or micro-tapered. | It influences draw-down and deformation after extrusion, especially important for the air-gap segment in dry-wet spinning. |
The Advantages of Trustech TIPS Spinneret
Highly controllable pore structure: By adjusting parameters such as diluent type and cooling rate, pore size (0.01–10 μm) and porosity (30% - 90%) can be precisely tuned, enabling diverse microstructures including open/closed cells, isotropic/anisotropic, and asymmetric architectures.
Compatible with hard-to-dissolve crystalline polymers: Designed for high melting point crystalline polymers without good room-temperature solvents, such as PVDF, PP, and PE. Utilizes a high-temperature melt-to-cooling phase separation pathway to achieve stable microporous membrane formation and industrial scale production.
High forming efficiency and superior mechanical properties: Compared with NIPS, the TIPS phase separation process is easier to control and enables faster membrane formation; the resulting fiber tensile strength is 2 - 4 times that of conventional processes (up to 6.21 MPa), suitable for manufacturing high strength UF and MF membranes.
Product Parameters
|
Brand |
Trustech |
Application |
TIPS/Melting |
| Material | SUS304, SUS630, SUS316L | Holes/Pack | 1-32 |
| Dope inlet Thread | G1/8, BSP1/8, NPT1/8 | Minimum membrane OD | 0.20mm |
| Bore liquid inlet thread | G1/8, BSP1/8, NPT1/8 | Customize thread | Yes |
| Precision | ±0.002mm | Concentricity | 0.003mm |
| Design | Conventional design/ FCT design | Connections | Standard |
| Viscosity application | 1000-300000cp | Roughness | Ra0.2-0.8 |
| Solvent | DMAC, DMF, NMP | Temperature | 260℃ |
Suitable Materials
PET(Polyethylene Terephthalate), PP (Polypropylene), PA6( Polyamide 6 ), PE (Polyethylene), PVDF( Polyvinylidene Fluoride), PS( Polystyrene), PI ( Polyimide),PA ( Polyamide, Nylon), PMP (Polymethylpentene), PBT ( Polybutylene Terephthalate), PTFE( Polytetrafluoroethylene)
Common Specifications
| No. | General Specification | Application | Design Type | Type |
| 1 | 1.4/0.8/0.6 | TIPS/Melting | Conventional design/ FCT design | Single-aperture/ Multi-aperture |
| 2 | 1.5/0.9/0.6 | TIPS/Melting | Conventional design/ FCT design | Single-aperture/ Multi-aperture |
| 3 | 1.6/1.0/0.6 | TIPS/Melting | Conventional design/ FCT design | Single-aperture/ Multi-aperture |
| 4 | 1.8/1.1/0.5 | TIPS/Melting | Conventional design/ FCT design | Single-aperture/ Multi-aperture |
| 5 | 1.9/1.2/0.6 | TIPS/Melting | Conventional design/ FCT design | Single-aperture/ Multi-aperture |
| 6 | 2.0/1.0/0.7 | TIPS/Melting | Conventional design/ FCT design | Single-aperture/ Multi-aperture |
| 7 | 3.1/1.8/1.5 | TIPS/Melting | Conventional design/ FCT design | Single-aperture/ Multi-aperture |
| 8 | 3.1/1.8/1.5 | TIPS/Melting | Conventional design/ FCT design | Single-aperture/ Multi-aperture |
| 9 | 3.2/2.2/1.8 | TIPS/Melting | Conventional design/ FCT design | Single-aperture/ Multi-aperture |
| 10 | 3.3/1.1/0.9 | TIPS/Melting | Conventional design/ FCT design | Single-aperture/ Multi-aperture |
| 11 | 3.4/2.4/2.0 | TIPS/Melting | Conventional design/ FCT design | Single-aperture/ Multi-aperture |
Customer Membrane Examples
ACHIEVEMENTS
FAQ
About Trustech