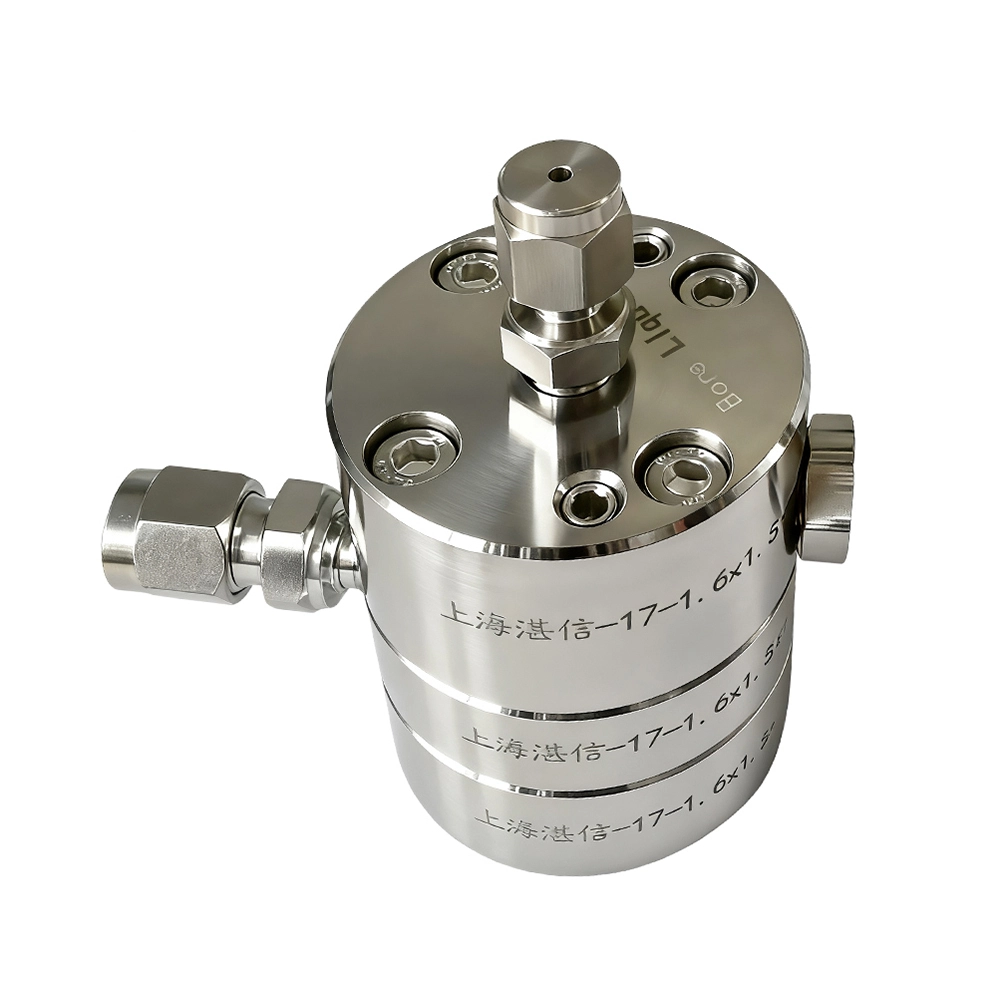
Polymer Fiber Spinning, Dual Layer Spinning Spinneret
Typical application scenarios
Membrane formation for separation, commonly referred to as co-extruded composite membrane or cast film spinnerets.
Hollow fiber membranes, flat sheet membranes, nanofiltration/ RO precursor membranes, and systems such as cellulose acetate, polysulfone, and PVDF.
Two or multi-layer co-extrusion to create a skin /selective layer, functional layers, and a support layer.
Trustech Spinneret Key Design Elements Trustech
These parameters are fundamental to spinneret design and directly determine the membrane's final performance
|
Parameter |
Description |
Influence on membrane performance |
| Flow channel (R) | The runner for transporting, buffering, and distributing the dope and bore fluids. | Different structures should be optimized according to material properties, viscosity, spinneret orifice size, and hole quantities to achieve optimal spinning performance. |
| Annular gap width (d) | The gap (thickness) of the dope flow channel. | It primarily determines the hollow fiber wall thickness. Narrower gaps yield thinner walls and lower mass-transfer resistance, but may reduce mechanical strength. |
| Bore tube outer diameter (d₁) | The outer diameter of the central tube forming the inner wall of the annular gap. | Together with the outer sleeve inner diameter, it defines the annular gap width. |
| Outer sleeve inner diameter (d₂) | The inner diameter of the spinneret outer sleeve forming the outer wall of the annular gap. | Together with the bore tube outer diameter, it defines the annular gap width and the fiber outer diameter. |
| Central tube inner diameter (d₃) | The diameter of the bore fluid channel. | It primarily determines the fiber inner diameter. The inner diameter affects membrane module packing density and the pressure drop of fluid inside the fiber. |
| Length-to-gap ratio (L/d) | The ratio of the flow channel length (L) to the annular gap width (d). | It affects spinning stability. Designing an appropriate L/d according to material properties and process conditions helps stabilize flow and eliminate entry effects, resulting in more uniform extruded fibers membrane. |
| Concentricity | The coaxial alignment among the dope layer inner diameter at the spinneret outlet and the bore tube inner and outer diameters. | It affects wall-thickness uniformity and bubble point pressure. |
| Extrusion face geometry | The foremost geometry of the spinneret, such as flat or micro-tapered. | It influences draw-down and deformation after extrusion, especially important for the air-gap segment in dry-wet spinning. |
The Advantages of Trustech Dual Layer Spinneret Trustech
One shot multi-layer co-extrusion: A single extrusion precisely stacks a dense selective layer over a porous support layer, with controllable layer thickness and interfaces. No downstream lamination or coating is required, simplifying the process and improving layer stability.
On demand material configuration for cost reduction: Use low cost, high volume resin for the support layer and only a small amount of high performance, higher cost material for the functional layer. Raw material costs drop by 30–50% while achieving high separation accuracy, high flux, and anti-fouling performance.
Robust interfacial fusion without delamination: Leveraging 0.003 mm concentricity machining precision and refined flow path design, the dope streams form clear, stably fused interfaces within micron-scale channels, ensuring strong interlayer bonding with no delamination risk and superior long-term structural and performance stability.
Product Parameters
|
Brand |
Trustech |
Application |
Dual layer |
| Material | SUS304, SUS630, SUS316L | Holes/Pack | 1 or 4 |
| Dope inlet Thread | G1/8, BSP1/8, NPT1/8 | Minimum membrane OD | 1.3mm |
| Bore liquid inlet thread | G1/8, BSP1/8, NPT1/8 | Customize thread | Yes |
| Precision | ±0.002mm | Concentricity | 0.003mm |
| Design | Conventional design | Connections | Standard |
| Viscosity application | 1000-300000cp | Roughness | Ra0.2-0.8 |
| Solvent | DMAC, DMF, NMP | Temperature | 150℃ |
Suitable Materials
PVDF (Polyvinylidene Fluoride), CA (cellulose acetate), PVC (Polyvinyl chloride), PES (Polyethersulfone), PSF/PSU (Polysulfone), PA (Nylon, Polyamide), PAN (polyacrylonitrile)
Structural Features
Dual layer dope spinneret is challenging to manufacture, requires high concentricity, and, when necessary, must withstand high temperatures and solvents such as DMAC and NMP.
We offer double material liquid hollow fiber membrane spinnerets used for producing composite membranes. The concentricity of these spinnerets are 0.003mm. The composite film covers a dense separation layer on the porous base film. The support layer and the separation layer use different materials, which makes it easy to obtain a separation membrane with a high separation function, high permeation flux, excellent resistance to pollution and an outstanding strength. We can also make films for specific functions using this process.
Common Specifications
| No. | General Specification | Application | Design Type | Type |
| 1 | 1.6/1.3/1.1/0.7/0.4 | Dual layer | Conventional design | Single-aperture/ Multi-aperture |
| 2 | 1.7/1.3/1.0/0.6/0.3 | Dual layer | Conventional design | Single-aperture/ Multi-aperture |
| 3 | 1.8/1.2/0.9/0.7/0.4 | Dual layer | Conventional design | Single-aperture/ Multi-aperture |
| 4 | 1.8/1.4/1.1/0.7/0.4 | Dual layer | Conventional design | Single-aperture/ Multi-aperture |
| 5 | 1.9/1.6/1.3/0.7/0.4 | Dual layer | Conventional design | Single-aperture/ Multi-aperture |
| 6 | 1.94/1.3/0.9/0.7/0.3 | Dual layer | Conventional design | Single-aperture/ Multi-aperture |
| 7 | 2.1/1.6/1.3/0.8/0.5 | Dual layer | Conventional design | Single-aperture/ Multi-aperture |
| 8 | 2.2/1.9/1.6/1.1/0.8 | Dual layer | Conventional design | Single-aperture/ Multi-aperture |
Customer Membrane Examples
ACHIEVEMENTS
FAQ
About Trustech