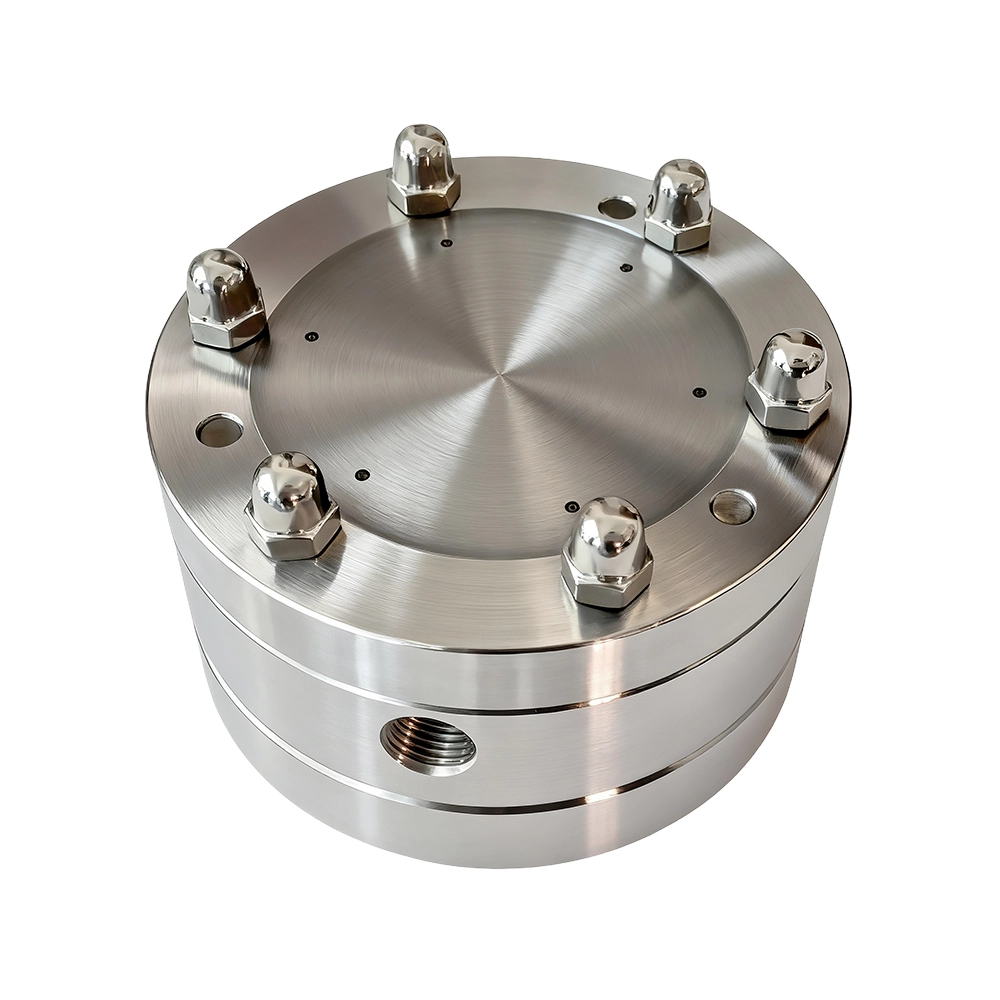
Polymer Fiber Spinning, Core Fiber Reinforced Spinning Spinneret
Product Overview
The spinneret enables three stream or multi-stream coaxial side-by-side co-extrusion: the outer layer is the polymer dope, the inner layer is the bore fluid, and simultaneously one or three reinforcing filaments are introduced. Through geometric constraint and tension control, a repeatable, uniform, and positionable "rib–matrix" composite structure is formed within the membrane wall.
Essentially, the spinning spinneret is a precision device for "multi-material co-extrusion, "distinct from built-in ribs , protrusions formed by the membrane itself, or post lamination reinforcement. It achieves one shot co-forming of the reinforcement filament and the membrane body, providing a dedicated solution to the insufficient dry/ wet strength and filament breakage issues of wet process NIPS membranes,especially polymeric ones.
Structural Features
Multi-channel coaxial design, precise reinforcement filament placement
Trustech Spinneret Key Design Elements Trustech
These parameters are fundamental to spinneret design and directly determine the membrane's final performance:
|
Parameter |
Description |
Influence on membrane performance |
| Flow channel (R) | The runner for transporting, buffering, and distributing the dope and bore fluids. | Different structures should be optimized according to material properties, viscosity, spinneret orifice size, and hole quantities to achieve optimal spinning performance. |
| Annular gap width (d) | The gap (thickness) of the dope flow channel. | It primarily determines the hollow fiber wall thickness. Narrower gaps yield thinner walls and lower mass-transfer resistance, but may reduce mechanical strength. |
| Bore tube outer diameter (d₁) | The outer diameter of the central tube forming the inner wall of the annular gap. | Together with the outer sleeve inner diameter, it defines the annular gap width. |
| Outer sleeve inner diameter (d₂) | The inner diameter of the spinneret outer sleeve forming the outer wall of the annular gap. | Together with the bore tube outer diameter, it defines the annular gap width and the fiber outer diameter. |
| Central tube inner diameter (d₃) | The diameter of the bore fluid channel. | It primarily determines the fiber inner diameter. The inner diameter affects membrane module packing density and the pressure drop of fluid inside the fiber. |
| Length-to-gap ratio (L/d) | The ratio of the flow channel length (L) to the annular gap width (d). | It affects spinning stability. Designing an appropriate L/d according to material properties and process conditions helps stabilize flow and eliminate entry effects, resulting in more uniform extruded fibers membrane. |
| Concentricity | The coaxial alignment among the dope layer inner diameter at the spinneret outlet and the bore tube inner and outer diameters. | It affects wall-thickness uniformity and bubble point pressure. |
| Extrusion face geometry | The foremost geometry of the spinneret, such as flat or micro-tapered. | It influences draw-down and deformation after extrusion, especially important for the air-gap segment in dry-wet spinning. |
The Advantages of Trustech Core Fiber Reinforced Spinning Spinneret Trustech
Precisely embed high strength reinforcing filaments to markedly improve mechanical performance
Enhances mechanical properties without sacrificing separation performance. One or three high-strength fine filaments are stably introduced into the membrane wall at the moment of spinning and co-formed with the matrix, significantly improving tensile strength and resistance to brittle fracture while maintaining the hollow structure and separation accuracy.
High precision multi-channel coaxial architecture for stable positioning and controlled forming
Independent multi-channel coaxial convergence, with filament channel dimensions closely matched to the filament diameter. Under tension and geometric constraints, a positionable "rib–matrix" composite structure is formed, avoiding filament exposure and non-uniform strength.
NIPS compatible process with stable lumen and reliable continuous production
Forced synchronous co-forming and optimized flow-path design ensure undisturbed phase separation, uniform pore structure (void fraction deviation ≤ 3%), and a non-collapsing lumen, enabling stable continuous spinning and high yield.
Product Parameters
|
Brand |
Trustech |
Application |
NIPS/Rib reinforced |
| Material | SUS304, SUS630, SUS316L | Holes/ Pack | Single hole |
| Dope inlet Thread | G1/8, BSP1/8, NPT1/8 | Minimum membrane OD | 1.2 |
| Bore liquid inlet thread | G1/8, BSP1/8, NPT1/8 | Customize thread | Yes |
| Precision | ±0.002mm | Concentricity | 0.003mm |
| Design | Rib reinforced conventional design | Connections | Standard |
| Viscosity application | 1000-300000cp | Roughness | Ra0.2-0.8 |
| Solvent | DMAC, DMF, NMP | Temperature | 150℃ |
Suitable Materials
PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate), PP (Polypropylene), PA6( Polyamide 6 ), PE(Polyethylene), PLA (Polylactide), TPU (Thermoplastic Polyurethane), PPS (Polyphenylene Sulfide), PTT (Polytrimethylene Terephthalate), PBT (Polybutylene Terephthalate), PVA (Polyvinyl Alcohol ), PAN (Polyacrylonitrile ), PEEK (Polyether Ether Ketone), PVDF-HFP ( Poly vinylidene fluoride-co-hexafluoropropylene)
Functional features
Optimized for wet-process NIPS, balancing strength and separation performance
Forced synchronous co-forming
By controlling the reinforcement filament feed speed to synchronize with the dope extrusion speed deviation ≤ 5%, the filament and dope are extruded simultaneously at the spinneret orifice and then enter the coagulation bath together to undergo phase separation. This ensures a tight interface between filament and membrane with no gaps or delamination peel off strength ≥ 5 N/cm).
Non-disruptive to phase separation
The flow channel design of the dope path, e.g., tapered outlet, filleted corners without dead zones, ensures uniform dope outflow, avoiding flow disturbances caused by the filament channel, thereby preventing membrane defects such as uneven porosity or pinholes and maintaining separation accuracy (e.g., MWCO deviation ≤ 10%).
Stable hollow structure
The annular gap between the bore-fluid and dope channels is uniform (deviation ≤ 0.01 mm). Even with added reinforcement filaments, the bore fluid can uniformly wet the inner surface of the dope to form a lumen with stable dimensions, void fraction deviation ≤ 3%, preventing lumen collapse or deformation.
Common Specifications
| No. | General Specification | Application | Rib reinforced conventional design | Type |
| 1 | 1.2/ 0.8/0.5 | NIPS/Rib reinforced | Rib reinforced conventional design | Single-aperture/ Multi-aperture |
| 2 | 1.3/0.7/0.4 | NIPS/Rib reinforced | Rib reinforced conventional design | Single-aperture/ Multi-aperture |
| 3 | 1.3/0.8/0.5 | NIPS/Rib reinforced | Rib reinforced conventional design | Single-aperture/ Multi-aperture |
| 4 | 1.3/1.0/0.7 | NIPS/Rib reinforced | Rib reinforced conventional design | Single-aperture/ Multi-aperture |
| 5 | 1.4/0.7/0.4 | NIPS/Rib reinforced | Rib reinforced conventional design | Single-aperture/ Multi-aperture |
| 6 | 1.4/0.9/0.6 | NIPS/Rib reinforced | Rib reinforced conventional design | Single-aperture/ Multi-aperture |
| 7 | 1.4/1.0/0.8 | NIPS/Rib reinforced | Rib reinforced conventional design | Single-aperture/ Multi-aperture |
| 8 | 1.6/0.8/0.5 | NIPS/Rib reinforced | Rib reinforced conventional design | Single-aperture/ Multi-aperture |
| 9 | 1.6/0.9/0.6 | NIPS/Rib reinforced | Rib reinforced conventional design | Single-aperture/ Multi-aperture |
| 10 | 1.8/0.9/0.5 | NIPS/Rib reinforced | Rib reinforced conventional design | Single-aperture/ Multi-aperture |
| 11 | 1.8/1.2/0.6 | NIPS/Rib reinforced | Rib reinforced conventional design | Single-aperture/ Multi-aperture |
| 12 | 1.8/1.2/0.8 | NIPS/Rib reinforced | Rib reinforced conventional design | Single-aperture/ Multi-aperture |
| 13 | 2.3/1.5/1.0 | NIPS/Rib reinforced | Rib reinforced conventional design | Single-aperture/ Multi-aperture |
| 14 | 2.3/1.5/1.2 | NIPS/Rib reinforced | Rib reinforced conventional design | Single-aperture/ Multi-aperture |
| 15 | 2.7/1.5/1.2 | NIPS/Rib reinforced | Rib reinforced conventional design | Single-aperture/ Multi-aperture |
| 16 | 2.2/1.7/1.4 | NIPS/Rib reinforced | Rib reinforced conventional design | Single-aperture/ Multi-aperture |
| 17 | 2.7/2.2/1.9 | NIPS/Rib reinforced | Rib reinforced conventional design | Single-aperture/ Multi-aperture |
Customer Membrane Examples
ACHIEVEMENTS
FAQ
About Trustech