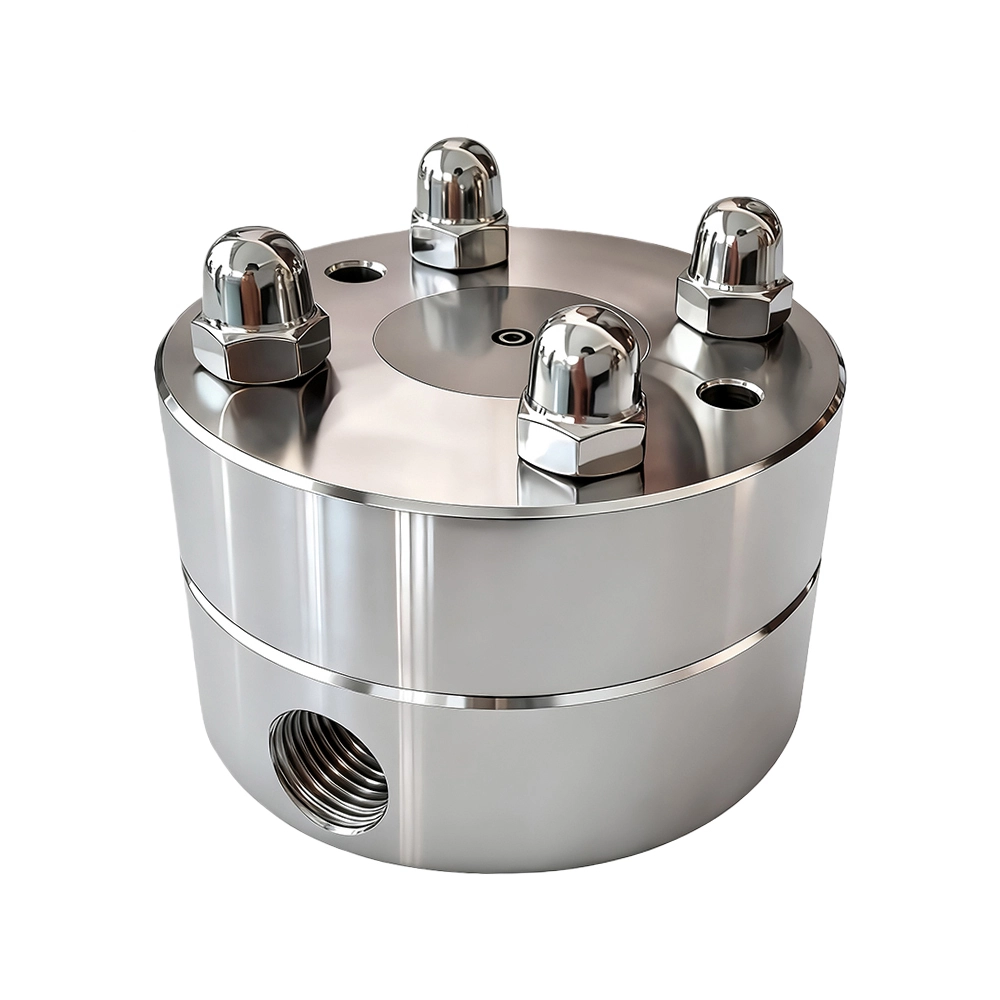
Polymer Fiber Spinning, Dry Jet Wet Spinning Spinneret
Structural features
Dual concentric needle, annular orifice
The center needle delivers the bore fluid (or N₂), while the outer annular slit extrudes the high viscosity spinning dope to form the hollow lumen.
Short conical inlet channel
L/D ≈ 1–2 with a cone angle of 60–90°, suppressing spinneret orifice swell and mitigating abrupt velocity gradients.
Heatable spinneret body
Equipped with 60–120°C circulating oil or cartridge heaters to ensure that high viscosity solutions >1000 Pa·s exhibit low viscosity and uniform flow at the orifice.
Adjustable air gap distance
Continuously adjustable 3–50 mm between the spinneret face and the coagulation bath surface, enabling optimization of the draw ratio,up to 20times.
Trustech Spinneret Key Design Elements Trustech
These parameters are fundamental to spinneret design and directly determine the membrane's final performance:
|
Parameter |
Description |
Influence on membrane performance |
| Flow channel (R) | The runner for transporting, buffering, and distributing the dope and bore fluids. | Different structures should be optimized according to material properties, viscosity, spinneret orifice size, and hole quantities to achieve optimal spinning performance. |
| Annular gap width (d) | The gap (thickness) of the dope flow channel. | It primarily determines the hollow fiber wall thickness. Narrower gaps yield thinner walls and lower mass-transfer resistance, but may reduce mechanical strength. |
| Bore tube outer diameter (d₁) | The outer diameter of the central tube forming the inner wall of the annular gap. | Together with the outer sleeve inner diameter, it defines the annular gap width. |
| Outer sleeve inner diameter (d₂) | The inner diameter of the spinneret outer sleeve forming the outer wall of the annular gap. | Together with the bore tube outer diameter, it defines the annular gap width and the fiber outer diameter. |
| Central tube inner diameter (d₃) | The diameter of the bore fluid channel. | It primarily determines the fiber inner diameter. The inner diameter affects membrane module packing density and the pressure drop of fluid inside the fiber. |
| Length-to-gap ratio (L/d) | The ratio of the flow channel length (L) to the annular gap width (d). | It affects spinning stability. Designing an appropriate L/d according to material properties and process conditions helps stabilize flow and eliminate entry effects, resulting in more uniform extruded fibers membrane. |
| Concentricity | The coaxial alignment among the dope layer inner diameter at the spinneret outlet and the bore tube inner and outer diameters. | It affects wall-thickness uniformity and bubble point pressure. |
| Extrusion face geometry | The foremost geometry of the spinneret, such as flat or micro-tapered. | It influences draw-down and deformation after extrusion, especially important for the air-gap segment in dry-wet spinning. |
The Advantages of Trustech FCT Dry Jet Wet Spinning Spinneret Trustech
Wear resistant and anti-clogging, compatible with high solids slurries: Nozzles and liners made from ultra-hard materials (zirconia, tungsten carbide, sapphire), with polished surfaces and anti-wear coatings, resist particle abrasion and clogging, ensuring stable delivery of high solids, viscous sols/slurries.
Low shear and rapid gel-forming: Gently curved distribution channels and a coaxial external gelling agent flow or short air-gap design significantly reduce shear stress to prevent premature gel aggregation; rapid gelation at the nozzle exit forms a robust green fiber wall, avoiding collapse and ovalization.
Multilayer co-extrusion with controlled shrinkage compensation: Supports multilayer co-extrusion (dense skin + porous support), producing composite ceramic/metal/glass hollow fibers in a single pass; spinneret dimensions and wall-thickness are pre-compensated for 10–40% drying/sintering shrinkage, maintaining dimensional accuracy and structural integrity after high-temperature sintering (400 - 1200°C).
Product Parameters
|
Brand |
Trustech |
Application |
Dry-jet wet spinning |
| Material | SUS304, SUS630, SUS316L | Holes/Pack | 1-32 |
| Dope inlet Thread | G1/8, BSP1/8, NPT1/8 | Minimum membrane OD | 0.20mm |
| Bore liquid inlet thread | G1/8, BSP1/8, NPT1/8 | Customize thread | Yes |
| Precision | ±0.002mm | Concentricity | 0.003mm |
| Design | Conventional design | Connections | Standard |
| Viscosity application | 1000-300000cp | Roughness | Ra0.2-0.8 |
| Solvent | DMAC, DMF, NMP | Temperature | 150℃ |
Suitable Materials
PVDF (Polyvinylidene Fluoride), CA (cellulose acetate), PVC (Polyvinyl chloride), PES (Polyethersulfone), PSF/PSU (Polysulfone), PA (Nylon, Polyamide), PAN (polyacrylonitrile)
Process characteristics
High positive drawing at the spinneret: low resistance in the air gap allows spinning speeds of 600 - 1200 m min⁻¹, which is 3–5 times that of pure wet spinning.
Uniform fiber structure: pre-solidification in the air gap forms a dense skin; bidirectional diffusion in the coagulation bath is moderated, reducing skin - core differences and overall porosity.
Suitable for high solids, high viscosity dopes: stable extrusion even at 18 - 30% solids and zero-shear viscosities of 2000–3000 Pa·s.
Flexible hole count: Spinning spinneret extend 1–6 holes for lab use, and 4-32 holes for industrial plates.
Common Specifications
| No. | General Specification | Application | Design Type | Type |
| 1 | 1.3/0.7/0.4 | dry-jet wet spinning | Conventional design | Single-aperture/ Multi-aperture |
| 2 | 1.3/0.8/0.5 | dry-jet wet spinning | Conventional design | Single-aperture/ Multi-aperture |
| 3 | 1.3/1.0/0.7 | dry-jet wet spinning | Conventional design | Single-aperture/ Multi-aperture |
| 4 | 1.4/0.7/0.4 | dry-jet wet spinning | Conventional design | Single-aperture/ Multi-aperture |
| 5 | 1.4/0.9/0.6 | dry-jet wet spinning | Conventional design | Single-aperture/ Multi-aperture |
| 6 | 1.4/1.0/0.8 | dry-jet wet spinning | Conventional design | Single-aperture/ Multi-aperture |
| 7 | 1.6/0.8/0.5 | dry-jet wet spinning | Conventional design | Single-aperture/ Multi-aperture |
| 8 | 1.6/0.9/0.6 | dry-jet wet spinning | Conventional design | Single-aperture/ Multi-aperture |
| 9 | 1.8/0.9/0.5 | dry-jet wet spinning | Conventional design | Single-aperture/ Multi-aperture |
| 10 | 1.8/1.2/0.6 | dry-jet wet spinning | Conventional design | Single-aperture/ Multi-aperture |
| 11 | 1.8/1.2/0.8 | dry-jet wet spinning | Conventional design | Single-aperture/ Multi-aperture |
| 12 | 2.3/1.5/1.0 | dry-jet wet spinning | Conventional design | Single-aperture/ Multi-aperture |
| 13 | 2.3/1.5/1.2 | dry-jet wet spinning | Conventional design | Single-aperture/ Multi-aperture |
| 14 | 2.7/1.5/1.2 | dry-jet wet spinning | Conventional design | Single-aperture/ Multi-aperture |
| 15 | 2.2/1.7/1.4 | dry-jet wet spinning | Conventional design | Single-aperture/ Multi-aperture |
| 16 | 2.7/2.2/1.9 | dry-jet wet spinning | Conventional design | Single-aperture/ Multi-aperture |
| 17 | 2.8/2.0/1.5 | dry-jet wet spinning | Conventional design | Single-aperture/ Multi-aperture |
| 18 | 2.8/2.2/1.9 | dry-jet wet spinning | Conventional design | Single-aperture/ Multi-aperture |
| 19 | 2.8/2.3/2.0 | dry-jet wet spinning | Conventional design | Single-aperture/ Multi-aperture |
| 20 | 2.9/1.4/1.1 | dry-jet wet spinning | Conventional design | Single-aperture/ Multi-aperture |
| 21 | 2.9/1.8/1.5 | dry-jet wet spinning | Conventional design | Single-aperture/ Multi-aperture |
| 22 | 2.9/1.9/1.6 | dry-jet wet spinning | Conventional design | Single-aperture/ Multi-aperture |
| 23 | 3.0/2.3/1.9 | dry-jet wet spinning | Conventional design | Single-aperture/ Multi-aperture |
| 24 | 3.0/2.3/2.0 | dry-jet wet spinning | Conventional design | Single-aperture/ Multi-aperture |
| 25 | 3.1/2.8/2.5 | dry-jet wet spinning | Conventional design | Single-aperture/ Multi-aperture |
| 26 | 3.2/2.2/1.8 | dry-jet wet spinning | Conventional design | Single-aperture/ Multi-aperture |
| 27 | 3.4/1.7/1.4 | dry-jet wet spinning | Conventional design | Single-aperture/ Multi-aperture |
| 28 | 3.4/2.2/1.8 | dry-jet wet spinning | Conventional design | Single-aperture/ Multi-aperture |
| 29 | 3.7/1.9/1.6 | dry-jet wet spinning | Conventional design | Single-aperture/ Multi-aperture |
| 30 | 3.8/2.2/1.9 | dry-jet wet spinning | Conventional design | Single-aperture/ Multi-aperture |
| 31 | 3.8/2.3/2.0 | dry-jet wet spinning | Conventional design | Single-aperture/ Multi-aperture |
Customer Membrane Examples
FAQ
About Trustech